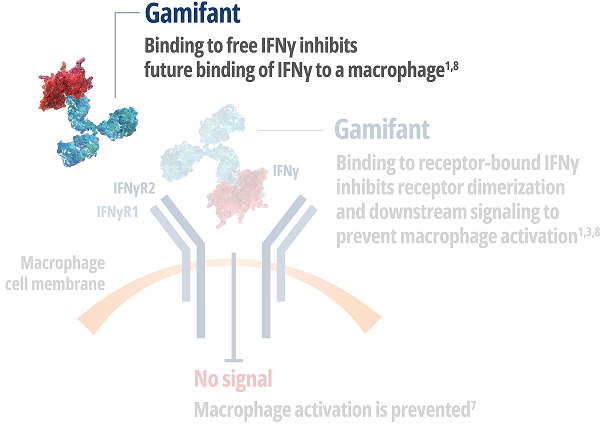
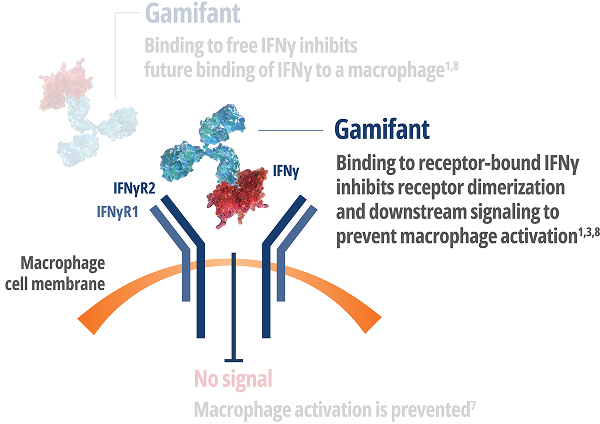
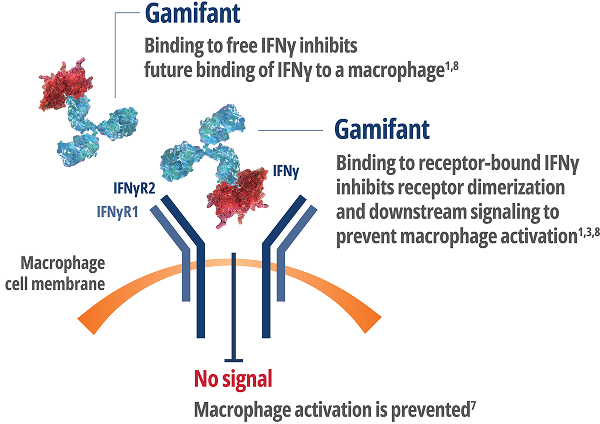
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Infections
Gamifant may increase the risk of fatal and serious infections with pathogens including mycobacteria, herpes zoster virus, and histoplasma capsulatum. Do not administer Gamifant in patients with these infections until appropriate treatment has been initiated.
In patients with primary HLH receiving Gamifant in clinical trials, serious infections such as sepsis, pneumonia, bacteremia, disseminated histoplasmosis, necrotizing fasciitis, viral infections, and perforated appendicitis were observed in 32% of patients.
In patients with HLH/MAS in Still’s disease receiving Gamifant in clinical trials, serious infections such as pneumonia, cytomegalovirus infection, cytomegalovirus infection reactivation, and sepsis were observed in 13% of patients.
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis risk factors and test for latent infection prior to initiating Gamifant. Administer tuberculosis prophylaxis to patients at risk for tuberculosis or known to have a positive purified protein derivative (PPD) test result.
Consider prophylaxis for herpes zoster, Pneumocystis jirovecii, and fungal infection while receiving Gamifant. Employ surveillance testing during treatment with Gamifant.
Closely monitor patients receiving Gamifant for signs or symptoms of infection, promptly initiate a complete diagnostic workup appropriate for an immunocompromised patient, and initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Increased Risk of Infection With Use of Live Vaccines
Do not administer live or live attenuated vaccines to patients receiving Gamifant and for at least 4 weeks after the last dose of Gamifant. The safety of immunization with live vaccines during or following Gamifant therapy has not been studied.
Infusion-Related Reactions
Infusion-related reactions in patients with primary HLH, including drug eruption, pyrexia, rash, erythema, and hyperhidrosis, were reported with Gamifant treatment in 27% of patients. In one-third of these patients, the infusion-related reaction occurred during the first infusion.
Infusion-related reactions in patients with HLH/MAS in Still’s disease, including pyrexia, headache, paresthesia, bone pain, pruritic rash, and peripheral coldness, were reported with Gamifant treatment in 13% of patients. Infusion-related reactions were reported as mild in 8% of patients and as moderate in 5% of patients.
Monitor patients for infusion-related reactions, which can be severe. Interrupt the infusion for infusion reactions and institute appropriate medical management before continuing infusion at a slower rate.
Adverse Reactions
Primary HLH
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 53% of patients. The most common serious adverse reactions (≥3%) included infections, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and multiple organ dysfunction. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2 (6%) of patients and included septic shock and gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
The most common adverse reactions were (≥10%) for Gamifant included infection (56%), hypertension (41%), infusion-related reactions (27%), pyrexia (24%), hypokalemia (15%), constipation (15%), rash (12%), abdominal pain (12%), CMV infection (12%), diarrhea (12%), lymphocytosis (12%), cough (12%), irritability (12%), tachycardia (12%), and tachypnea (12%).
HLH/MAS
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 12 patients (31%), with the most common serious adverse reaction being pneumonia (5%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in two patients (5%) and included multiple organ dysfunction and circulatory shock.
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) for Gamifant included viral infection (44%), rash (21%), anemia (18%), leukopenia (15%), thrombosis (15%), bacterial infections (13%), headache (13%), hyperglycemia (13%), infusion-related reactions (13%), abdominal pain (10%), hypertension (10%), pyrexia (10%), and thrombocytopenia (10%).
Click here for full Prescribing Information for Gamifant.
You may also contact Sobi at medinfo.us@sobi.com or 866-773-5274.
For statutory pricing disclosures, visit sobi.com/usa/en/state-disclosure-requirements