Pivotal Trial
Study design in primary HLH
Gamifant demonstrated efficacy and safety in a pivotal trial1
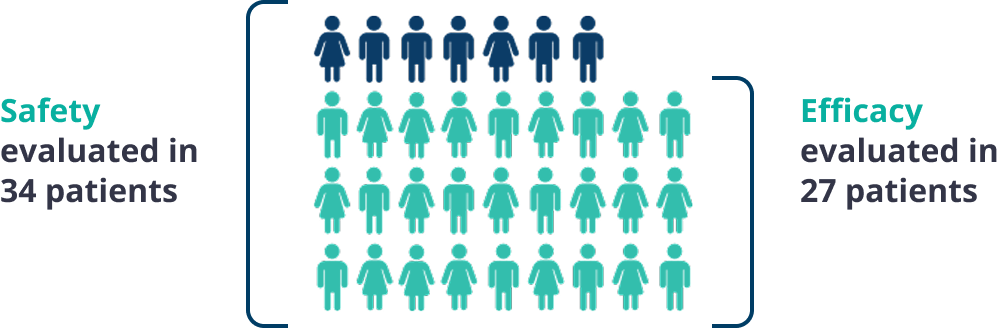
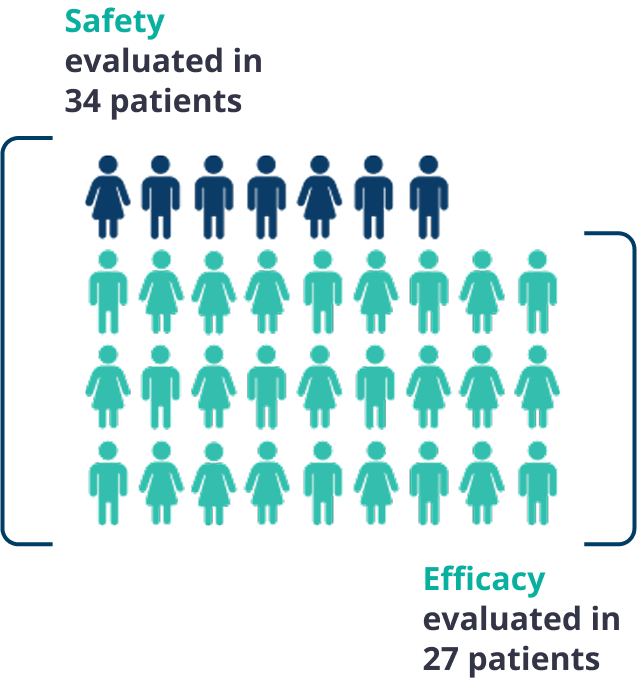
The safety and efficacy of Gamifant were evaluated in a multicenter, open-label, single-arm study.1
Studied in patients with significant unmet need1
Patients enrolled in the Gamifant pivotal trial had either suspected or confirmed primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) based on 5 of the 8 HLH-2004 criteria with no evidence of malignancy, molecular diagnosis, or family history consistent with primary HLH.
In addition, the treating physician assessed patients as having at least one of the following: refractory disease, recurrent disease, progressive disease, and/or intolerance to conventional therapy.
A diagnosis of primary HLH was suspected in 18% of patients based on the HLH-2004 diagnostic criteria with no evidence of malignancy. Diagnosis was genetically confirmed in 82% of patients.
The most frequent causative mutations were FHL3-UNC13D (n=7; 26%), FHL2-PRF1 (n=5; 19%), and Griscelli syndrome type 2 (n=5; 19%).1
The median age of patients in the study was 1 year.
Patients ranged in age from 0.2 years to 13 years old.1
27 of 34 patients received conventional therapy prior to enrollment, with a median of 3 prior agents.
Prior regimens included combinations of dexamethasone, etoposide, cyclosporine A, and antithymocyte globulin.1
The median duration of Gamifant treatment was 59 days.
Duration of treatment ranged from 4 to 245 days in 34 patients studied for safety.1
Primary endpoint1
The primary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR) at end of treatment. ORR was defined as achievement of either complete or partial response or HLH improvement and evaluated using an algorithm of objective clinical and laboratory parameters.
Complete response
defined as normalization of all HLH abnormalities (ie, no fever, no splenomegaly, neutrophils >1x109/L, platelets >100x109/L, ferritin <2000 μg/L, fibrinogen >1.50 g/L, D-dimer <500 μg/L, normal CNS symptoms, no worsening of soluble CD25* >2-fold baseline)
Partial response
defined as normalization of ≥3 HLH abnormalities
HLH improvement
defined as ≥3 HLH abnormalities improved by at least 50% from baseline
CD=cluster of differentiation; CNS=central nervous system.
*Soluble CD25 is also referred to as soluble interleukin-2 receptor.
Key secondary endpoints
Secondary efficacy endpoints included the time to response, duration of response, and the number of patients proceeding to transplant.2